Web Socket Overview
Web Socket Overview
What is Web Socket
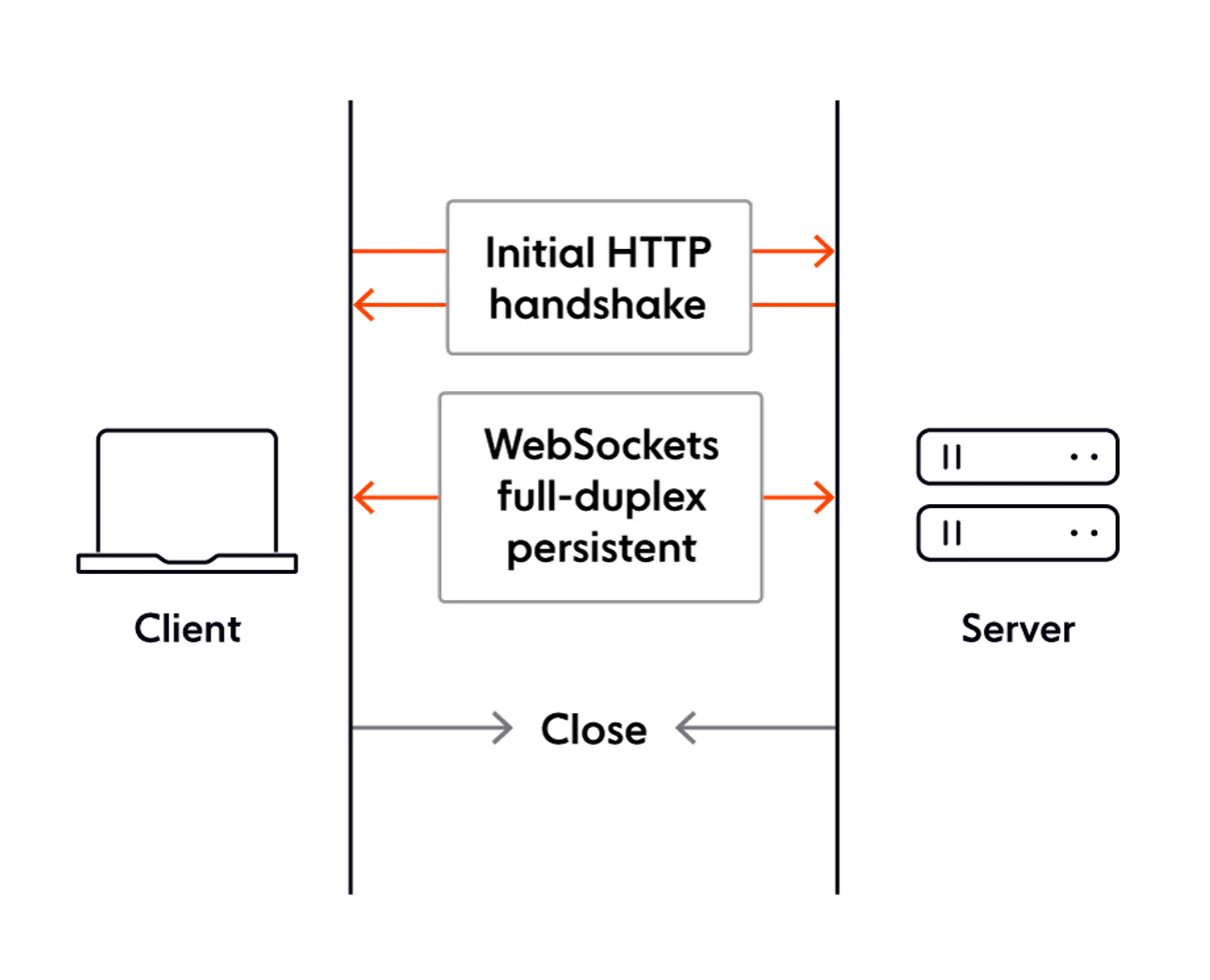
- It is a Bidirectional, full Duplex protocol to communicate between client and server over the web
- It is used in Chatting, notifications, real-time feeds, multiplayer gaming
HTTP 1.0
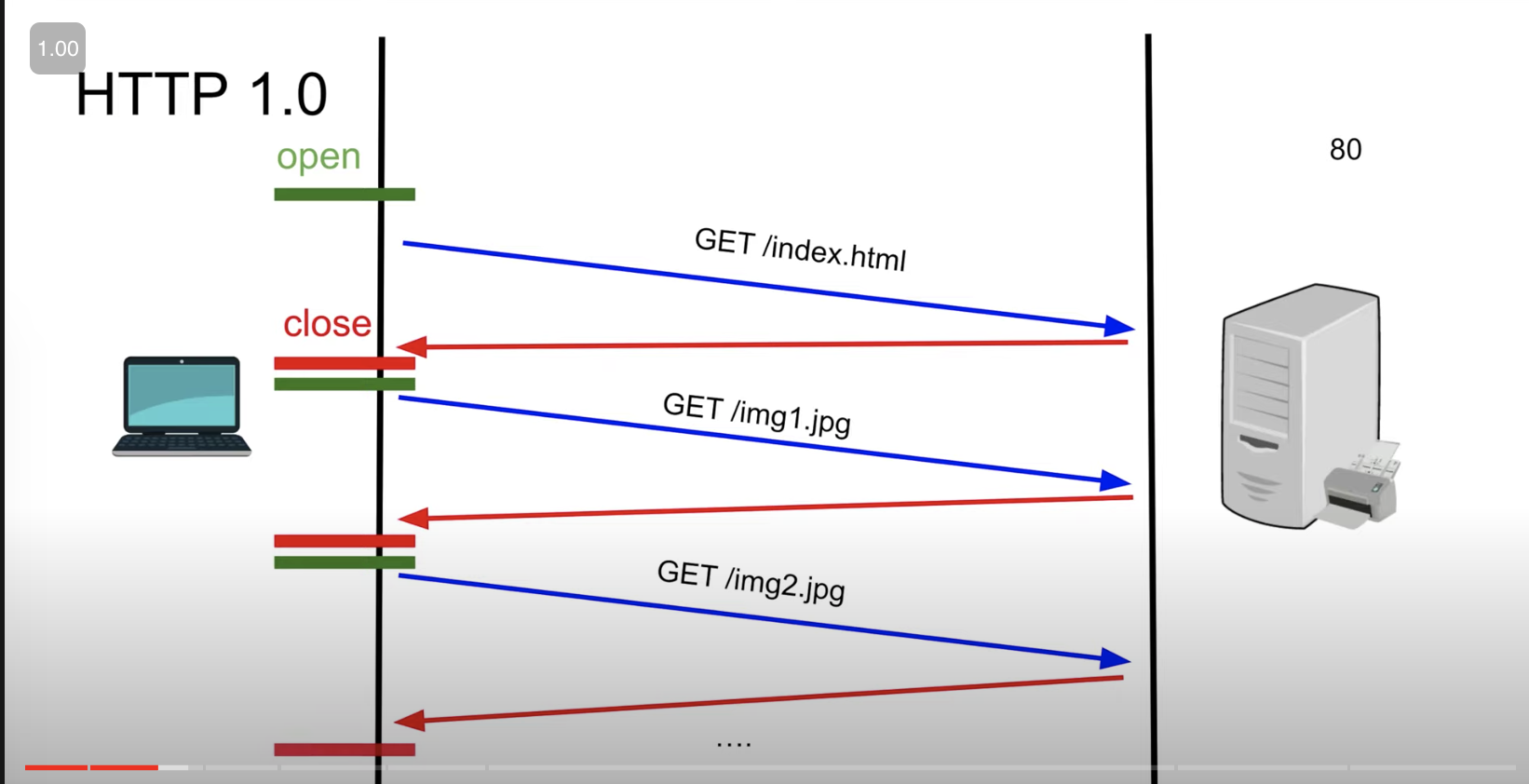
- HTTP Protocol 1.0 Recap, is built on TCP protocol when it was first built as a request-response system
- The Server cannot randomly send requests to clients it needs to be requested for something to respond to ie client has to initiate the request first
- After Each Request, the connection is closed and for each request, the connection has to be established again
- Consider the example where the client requests 10 images for each request the server will (open and close connection) x10 for each image to receive which is costly for the server and the client
HTTP 1.1
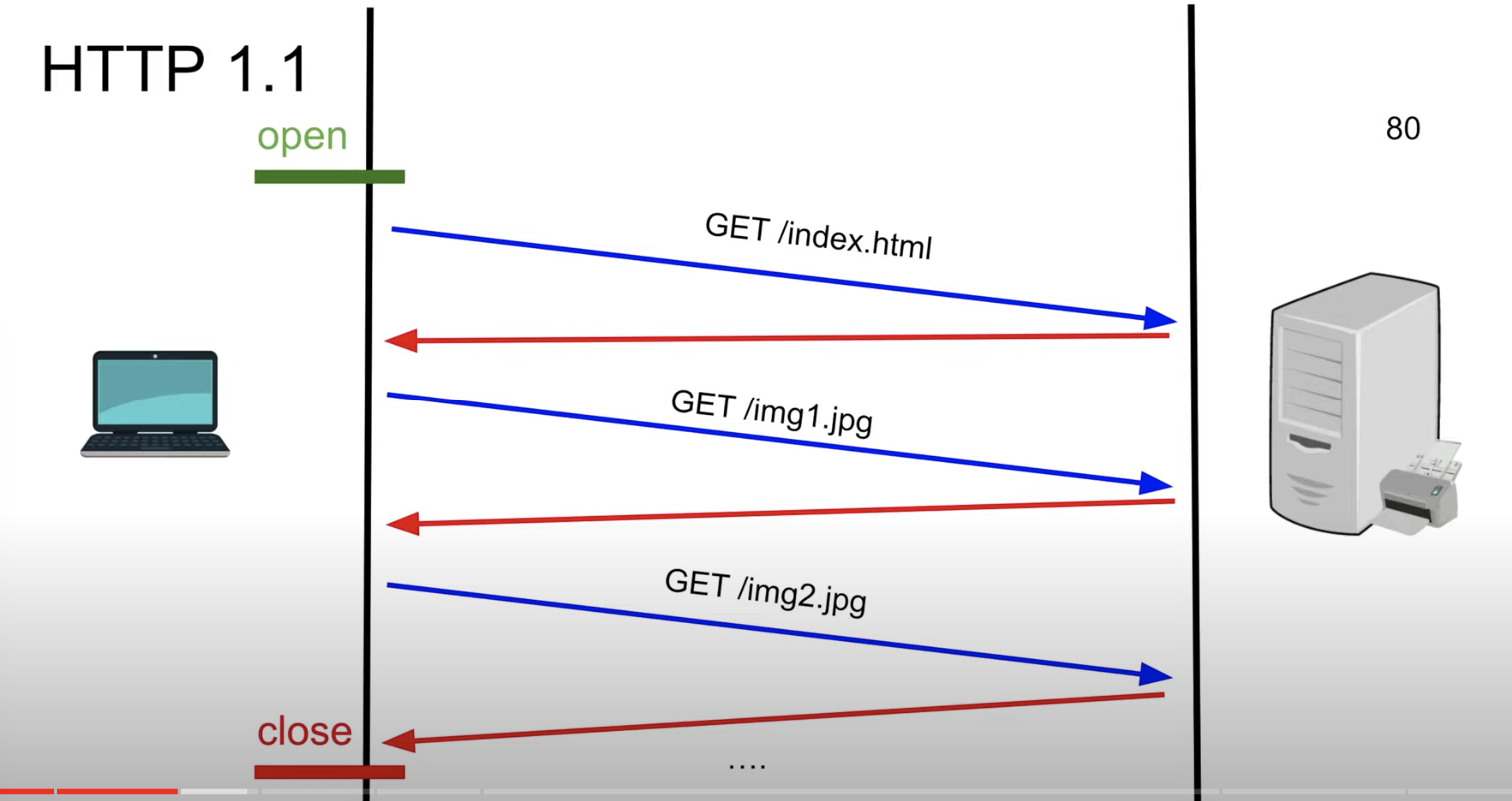
- Realizing the previous implementation of HTTP 1.1 was made which once made a request to keep the connection open
- It keeps the connection open using the Header “ keep-alive” in the header which is an epithermal header and cannot be propagated through proxies
- Once a Connection is made it remains open and subsequent requests can be made using the same TCP connection
- We Close the connection once not needed
Web Sockets
- Web Socket uses HTTP 1.1 between client and server
- It’s a stateful protocol since the client and server are both aware of each other
- HTTP is Stateless
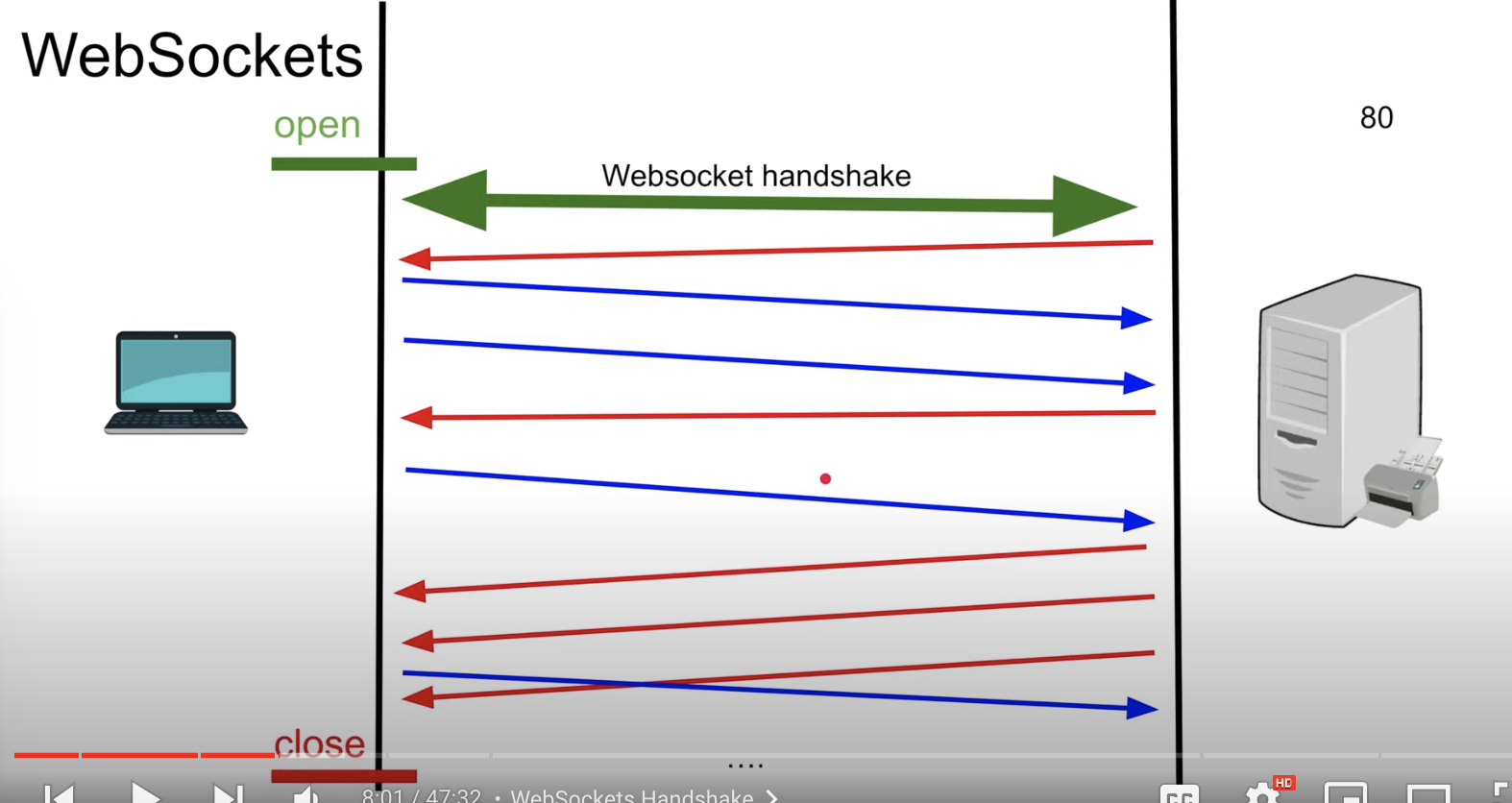
- We open a connection and do a Websocket Handshake
- Once the WebSocket handshake happens it detach from HTTP and becomes a binary protocol
- Anyone can send data to anyone, using the underlying TCP connection API
- The client can send all data to the server
- The server can send all data to the client
- Both can concurrently send data to each other etc etc
WebSockets Handshake
- WS:// or wss:// similar to HTTP and HTTPS
- The First request we make is normal HTTP GET request, which asks the server to upgrade to 1.1
- The Server will reply 101 Switching protocol, and become binary protocol
- The key is used for seeding and hashing to generate a new key
- Can you use the Existing Server or a do it manually to implement the same
WebSockets use cases
- Chat Application
- Live Feed
- Multiplayer gaming (Multiple clients means maintaining multiple states ie scaling stateful is difficult )
- Showing client progress/logging
Example Implementing WebSockets in Node JS
Web Sockets Pros and Cons
Pros
- Full-duplex (no polling), not have to ping the server all the time to get some status or progress update
- HTTP compatible
- Firewall friendly (standard) (80 if Insecure ) (443 when Secure)
Cons
- Proxying is tricky L7, have to break the connection and create another to the backend (L4 works better)
- L7 load balancing challenging (timeouts)
- Stateful, difficult to horizontally scale
Do we Have to use a Web Proxy?
- No !, Rule of thumb - do we absolutely need bi-directional communication
- Long polling
- Event Source
Reference
This post is licensed under CC BY 4.0 by the author.