Spring Boot Notes
Spring Boot
Before Spring
- Java Beans, POJO
- Lacked in Security and Transaction Management
- Then came enterprise java beans EJB
- Solved Transaction processing
- Session Processing
- EJB development was not easy
- Spring Emerged as answer
Intro to Spring
Spring is an open-source lightweight framework , main technologies used by Spring Framework for developing enterprise applications
- Aspect-Oriented Programming AOP
- Enables cross-cutting concerns in a centralized area
- POJO
- Dependency Injection DI
- Java enterprise edition specification
Spring Framework
- Relies heavily on Inversion of Control
- Build using POJO - plain old java object
- Spring works with java Standard edition
- POJO+ configuration Metadata = Spring container
- A Spring bean is a basic building block that is managed by Spring Framework
- Spring is responsible for creating and destroying beans
- Providing dependencies of the bean which could be other beans or configuration properties
- Intercepting Bean method calls to include additional framework features
What makes spring powerful?
- How it manages dependencies
- Design patterns are the responsibility of developers , solution Inversion of Control ie role of managing dependencies is handled over to Spring framework
What is Inversion of Control (IoC)?
A process by which objects define their dependencies and an external container injects those dependencies into the object , the object need to worry about where its dependencies are coming from
It is also called dependency injection where we let the spring container instantiate objects
Spring Features
IoC Container (Inversion of Control)
- It is a process by which an object defines its dependency (ie the other object they work with either through constructor argument or simple property )
- The Container Injects the dependency when the bean is being created
- It is a core container that uses dependency injection to implicitly instantiate objects during runtime
- This container also handles configuration management of application objects
- The process is Inverse therefore the inversion of container
Spring MVC Framework
- Create web applications using MVC architecture
- All requests made by the user goes through a controller and gets dispatched to model or view based on the mapping
- This framework can be integrated with all frontend technologies
Data Access Framework
- It allows the developer to use persistence API such as JDBC or hibernate to store or access data in the database
- Interacting with database, connection, closing the connection ie all the keys concerning an interaction with the database or exception handling along with transaction management can be handled easily with data access framework
Transaction Mangement
- Provides Java Transaction API , JDA for global and local transaction
- Create a wide range of transactions on basis of Spring declaration transaction management
Spring web service
- A powerful mechanism for distributing messages between two machines
- It generates web service endpoints based on java classes provided
JDBC abstraction layer
- Handles error in an easy and efficient way
- Reduce the JDBC programming
Spring TestContext Framework
- Do unit and integration testing
- provide key integration testing functionalities such as
- Context Management
- Caching Dependency Injection of the test fixture
- Supports transactional test management
- Default Rollback Semantics
Spring Code Module
- Core component of spring framework provides the IoC container
- there are two types of implementation of spring containers
- Bean Factory
- It acts as a single IoC Container for instantiation application objects
- It also configures and assembles dependencies between these objects
- Application Context
- It provides a central configuration for an application
Spring ORM Module
- Used for accessing data from databases in an application
- It provides supports for various ORM frameworks like Hibernate
- Simple declarative transaction management, resource management, and transparent exception handling
Spring AOP Modules
- Object Oriented programming breaks the program into a hierarchy of objects
- Whereas AOP break it into Aspects or concerns
- They are typically denoted with aspect annotation
- Aspect Helps developer implement cross-cutting concerns in a centralized fashion , rather than implementing similar objects in multiple places
Spring MVC Modules
- Implements MVC design
- request from the browser goes to dispatcher servlet which then sends it to a controller based on a set of Handler mapping
- the Controller process the application and returns the response to the dispatcher servlet in form of the model object
- Dispatcher servlet uses view resolver to send back the response
Spring WEB Flow Module
- It is an extension to the spring MVC model
- It helps in defining flow between the different user interfaces in the application
- Helps virtually split up an application into different modules and use them accordingly
Spring DAO Module
- It introduces JDBC abstraction layer by eliminating the need for boilerplate coding
- it supports a programmatic and declarative approach to transaction management
- Easier support to access the database resources
Spring Application Context Module
- This is based on the core module of the spring framework , it supports the features from the bean factory and other features such as:
- Internationalization
- Validation
- Resource Loading
- Implements message source Interface and provides messaging functionality to an application
Model View Controller Design Pattern
- Data access layer
- Service Layer
- Presentation Layer
Spring Boot
- Inversion of Control
- Dependency Injection
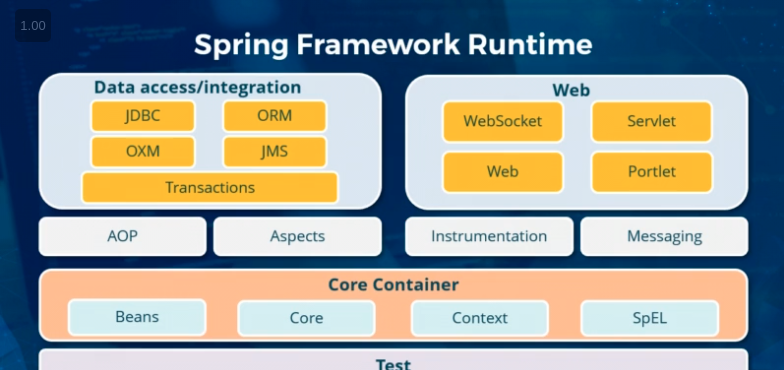
Spring Framework Modules
1. Core Container
- The core container is responsible for managing beans
- Sets up the context of the application
- Special Expression language “SpEL”
- All other projects are built on top of the core container
- Spring-core and spring-beans for IoC and dependency injection
- Application Context eliminates singletons and decouple components
- spring-context for access to objects in JNDI (Java Naming and Directory Interface) registry style
- spring-expression for working with the object at runtime
2. Data Access and Integration
- spring-JDBC abstracts away vendor-specific error codes and handling
- spring-orm for working with Java-Persistence API (JPA) , Hibernate, and other ORM API’s
- spring-JMS, spring messaging for message processing
- spring-tx for working with POJO declaratively
3.Messaging
- spring-messaging module
- Message, MessageChannel and MessageHandler abstraction
- Annotations for mapping messages to methods
- Similar to Spring MVC annotation based programming
4. Web
- spring-web , spring-web MVC, and spring-WebSocket modules
- spring-web for basic web features eg, servelet listeners , HTTP client
- spring-web MVC for web application programming using MVC paradigm
- spring-WebSockets as a thin lightweight layer above TCP
(AOP) Aspect Oriented Programming
- Programming paradigm that adds new “ aspects” to the behavior of existing code using “pointcuts” (external specifications)
- This ensures existing code is not modified to add new behavior
AOP in Spring
- AOP alliance-compliant aspect-oriented programming
- Add additional functionality using interceptors , pointcuts, and source-level metadata
- Implement aspects with @Aspect annotation
- Spring AOP modules helps combine OOP with AOP
5. Testing
- Unit-testing as well as integration testing
- Junit or TestNG
- Loading and caching of Application Context objects
- Mock objects to test code in isolation
Dependency Management
Dependency management specify what JAR (java archives ) and libraries our project depends upon
- process of correctly getting all required jar files into the correct location (and into classpath) so that spring works correctly
- Extremely important and somewhat tricky to get right
- Dependencies include compiling time as well as run-time
- Different and distinct from dependency injection
- Deals with physical resources (files)
- Direct vs transitive dependencies
- Transitive dependencies are hardest to manage
- Need a copy of all jar libraries for Spring
- Separated into modules, use what is needed
- Spring publishes artifacts to Maven Central
- Maven Central can be thought of as a repository for JAR files
- Also publishes to specific public Maven repo
- Either use Maven, Gradle, or Ivy
- Install manually or use any above tool above
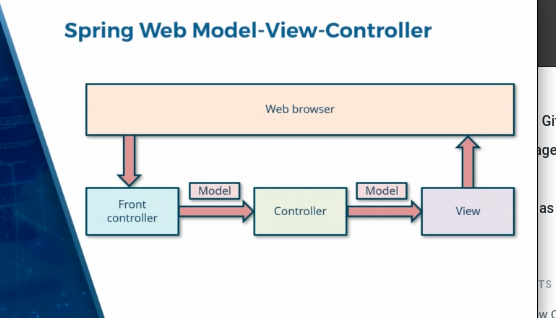
Model View Controller
- Spring MVC or Spring Web MVC, model-view-controller paradigm for building web apps
Model
Models contain the application data as POJO
- Encapsulates application state (but not application logic)
- Can be queried to obtain state
- Notified by the controller when the state needs to change
- Notifies controller once the state has been changed
Controller
Handles the user request and act as a router between the model and the view
- Defines application logic (not application state)
- Maps user actions to state changes
- Updates application state only via model (not directly)
- Updates views once application state has changed
Views
Renders the output Data from the model in a presentable format
- Present application state to users via an appropriate interface
- Allow users to interact with the state, modify the state
- Do not store application data (except for caching)
- Built using reusable and configurable element
Each component when updated notify the listener via Synchronous methods vs. Asynchronous events
Spring MVC Framework
Based on Model, View Controller Design Pattern
Spring framework relies on three underlying technologies, along with the web features, it also supports the core functionality of spring frameworks such as IoC and dependency injection
- Model - Model is typically your application data, it can be a single or a collection of objects
- Controller - acts as a router between model and view and it contains all the business tools of the application, any class marked with @Controller annotation will make it a controller class
- View - it represents the information in a particular format, JSP is an example of creating a view page
- Front controller - DispatcherServlet works as a Front controller and it is responsible for managing the flow of the Spring MVC application
- one of the key components of Spring MVC is the DispatcherServlet and it is a class that receive all the incoming requests and maps it accordingly to the model and the controllers
Spring MVC Execution Flow
- Dispatcher Servlet receives the incoming request
- Dispatcher servlet identifies the controller class based on the handler mappings
- Once the controller has been identified the request gets processed
- After processing it returns the model data and the exact view name
- Dispatcher Servlet sends the model data to the view resolver to determine the view page
- Dispatcher Servlet returns the view page
Advantages of Spring MVC
- Separate roles - Spring MVC defines separate roles for the different components
- Powerful configuration - It provides robust configuration support for context references, web controllers, business objects, and validators.
- Light Weight - Uses lightweight servlet container to develop to deploy your application with all the easy configuration and reduced boilerplate coding
- Rapid development
- Ease to Test - by injecting the data using the setter methods
- Reusable business code - instead of creating new logic, use existing business objects
- Flexible Mapping - with help of annotations, mapping the configurations, redirections are very straightforward
Disadvantages of Spring MVC
- Steep learning curve
- Framework version instability
- Dependency injection (entire project dependent on spring framework)
Components
- Servlets
- JSP (Java Server Pages)
- JSTL (Java Pages standard tag library)
Servlets –> JSP –> JSTL (collection of useful JSP tags for common tasks)
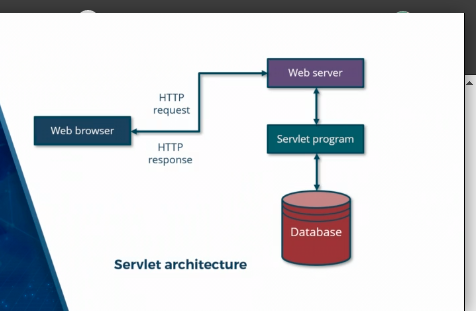
Servlets
- used to build dynamic web pages in java
- existed since 1996, when most web pages were static
- Run on a Java-enabled web or app server
- Handle incoming HTTP requests
- Servlet (Java program) runs within the environment of Servlet Engine
- Servlet Engine also referred to as Servlet Container
- Deals with cookies and MIME types
- Support for session management and security
JSP , Java Server Pages
- Java ServerPages is an abstraction on top of servlets
- JSP scriptlet is a basic unit -enclosed in tags <% ……%>
- JSP scriptlet will be injected into a servlet at runtime
- Servlet corresponding to JSP scriptlet will be cached and re-used until JSP is modified
- JSP Compiler is needed to compile JSP scriptlets to servlet
- JSP compiler runs on java-enabled web app or server
- Servlet code runs inside JVM on the webserver
- JSP allows Java code and HTML to be interleaved
JSP Standard Tag Library aka JSTL
- Sciptlet tags are basic building blocks of JSP
- JSTL is a standard library for JSP tags
- Taglibs contains the core functionality of JSTL
- Taglibs ship with every servlet and JSP framework
JSTL Tag Classification
- JSTL Core : loops , control flow ,<div> output
- JSTL Formatting : dates, internationalization
- JSTL SQL : use usually discouraged (security)
- JSTL XML : working with XML documents
- JSTL functions : mainly string manipulation
Model View Controller
- Dispatcher Servlet as a front controller to receive browser requests
- Dispatched to the appropriate controller via handler mappings
- Result returned to the user via ViewResolver Classes
Typical Spring MVC App
- Model - Pojo (Plain old java object)
- Views - JSP templates written with JSTL
- Controller - Dispatcher Servlet
- useful for classic 3 tier architecture
REST based Controller
REST (Representational State Transfer) is an architectural style that uses HTTP resources to create a REST web service
@RestController
- Used to create controller component
- Serve as an entry point for handler mappings
@ResponseBody
- Return value for the HTTP response object
- Spring will convert the return value to HTTP response based on the content type in the header, like JSON
- One of the key classes that represent the entire HTTP response is response Entity
- All return types along with corresponding response code can be customized with this class
@RequestBody
- It is similar to the response body
- Spring binds the incoming HTTP request to the annotated parameter
- Converts the request into domain object based on the content type in the header
@PathVariable
- Denotes the method parameter that will be bound to the resource URL
Spring HTTP Methods
- HTTP GET
- HTTP PUT
- HTTP POST
- HTTP DELETE
Spring MVC Rest API Advantages
- Follows MVC architecture but all requests are handled through a controller
- Enables sepration of logical component for easier maintainence
- Dedicated Annotation allows defining configurations easily
- Bypass view based rendering
- Path variable annotation
- Resource repsresentation
- Request body annotation
- REST template class
Spring Data
- Provides a familiar and consistent programming model for a developer to access the datastore
- Spring Data reduce the boilerplate coding
- Provides powerful repository and custom mapping abstraction
- Easy Integration with other spring modules
- Dynamic Query Generation from the method names
- Support wide range of persistent store
- Relational Database
- Non-Relational Database
- Map-Reduce framework
- Cloud-based data service
Java Persistent API
- It is an object-relational mapping standard created for Java to store access and manage objects in a relational database
- Spring Data adds layer on top of the JPA for easier integration with other spring modules
- JPA reduce boilerplate coding
- Focus more on business logic than configuration
Features of JPA
- Spring data support type-safe queries that enforce data type validation
- It supports the ability to keep track of who created or changed an entity and the point in time this happened
- Pagination support, where data from large result sets is returned in chunks based on page size and number
- Dynamic Query execution using API suggest JPA criteria
- Support for XML based entity mapping for configuration files
Spring Data LDAP (Lightweight directory access protocol)
- LDAP directories are hierarchical data stores used for storing user information to support authentication and authorization
- used java-based classes or XML namespace
- Annotation based mapping metadata
- Automatic implementation of repository interfaces
- Support QueryDSL Integration
Spring Data Elasticsearch
- Uses POJO for interacting with an elastic search model
- Elasticsearch documents
- Repository access layer
- XML based, object mapping integrated with spring conversion services
- Automatic implementation of repository interfaces
- Context and dependency injection support while interacting with repositories
Spring for Apache Hadoop
- Spring provides a unified configuration model and easy to use API
- Enabling integration with other spring objects enabling the developers to building solutions for big data
- HDFS is a distributed file system that provides high-performance access to all data across the Hadoop clusters
- MapReduce is a framework supported by Hadoop for processing huge amounts of data in parallel
- Apache Pig is a platform that analyzes large sets of data that consists of a high-level language for expressing data analytics programs
- Apache Hive is a data warehouse for providing data query and analysis, it provides a SQL like an interface for querying the data stored across different file systems and database
Spring Security
- It is a Java Enterprise edition framework for securing enterprise Spring-based application
- Provides features for both authentication and authorization
- Servlet API Integration
- Web Attack prevention (session fixation,clickjacking,cross-site request forgery )
- Supports Integration with Spring MVC
Authentication
- Mechanism to verify or establish your identity
- Common method to do so is using user credentials
- Various forms of Authentication
- Single Factor Authentication - requires password
- Two Factor authentication - password + other info
- Multi Factor Authentication - password+ info+ passcode
Authorization
- It is the process to determine whether the authenticated user has access to a particular resource or not
- Access control for URL
- Secure object and methods
- Access control lists
Spring Security OAuth
- OAuth Providers
- OAuth consumer
- Supports OAuth1(a)
- Support for OAuth 2.0
Spring Security SAML
- Security Assertion Markup Language Authentication and federation mechanism in a single application
- Supports SAML 2.0 which uses security tokens containing assertions to pass the principal user information between the service provider and identity provider
- IDP (identity provider )and SP (service provider)single sign-on
- Service provider metadata generation
Spring Bean
- Spring bean is a simple object that is instantiated, Assembled, and Managed by the IoC container
- The Container Injects the dependency when the bean is being created
- The process is Inverse therefore the inversion of container
- Bean Factory interface is the central IoC interface in spring
- It is the actual representation of the spring IoC container responsible for managing the beans
- The most commonly used BeanFactory interface is bean factory class using XML
- Spring configuration contains at least one configuration that the container must manage
- There will be more than one bean definition with the XML configurations and these beans are configured as elements in the bean tag
- Configuration metadata informs the spring container on how to instantiate, configure and assemble objects within your application
- The configuration metadata is maintained in XML format
- Instantiating Spring IoC container is straightforward can be achieved with the use of application context
- Spring also supports annotation-based configuration for bean creation
Spring Bean Definitions
- Bean Definitions are represented as bean definition objects which contains a qualified package name, which is the actual implementation class of the bean being defined
- Behavioural configuration elements which states how the bean should behave in the container
- References to other Beans which are needed for the beans to its work, these references are also called collaborators or dependencies
- Other Configuration Settings to set in the newly created object, best example is managing a connection pool
Spring Bean Definition Inheritance
Inheritance is ab object-oriented programming mechanism where an object is created or derived from another class which is usually a parent-child relationship
- A Bean definition contains a large amount of configuration information, including container-specific information , constructor arguments, and property values
- A child bean definition on the other hand is a bean definition that inherits the configuration data from a parent definition
- Child bean definitions can overwrite values if needed
- Bean Factory - child bean definitions are represented by the ChildBeanDefinition class
- Most Developers configure bean declarations in XMLBeanFactory
- _**_When using XML-based configuration metadata a child bean definition is indicated simply by using the parent attribute
- Configuration Information, some of the configuration information for bean definition inheritance are scope, constructor arguments, properties , and over overriding methods
- ChildBeanDefinitions, A child bean definition will use the bean class from the parent definition if none is specified
- At the same time, it can also override it
- Child Beans have to be compatible with the parent
- It will inherit constructor argument values, property values, and the method override from the parent
- It also has option to add new values if needed
Spring Bean Scopes
When a bean definition is created we are instantiating a class , Along with dependencies and configuration, Spring allows us to control the scope of the application as well
Spring Support 5 different scopes
- Singleton Scope- only one object instance will be created for the single bean definitions
- Prototype Scope- scopes a single bean definition to any number of object instantiations
- Request Scope - Request scope is valid until the lifecycle of a single HTTP request, each and every HTTP request will have its instance of the bean
- Session Scope - works throughout the lifecycle of the HTTP session , the best example of session scope is when a user tries to login into an application and the session is valid until the user decides to log out or close the application
- Global Session - scopes a single bean definition to the lifecycle of a global HTTP session, this is only valid when the web application is under the application context
Spring Boot Auto-configuration
- @ConditionalOnClass - check dependencies on specific classes before creating auto-configured beans
- @ConditionalOnProperty - check dependencies on properties before creating auto-configured bean
- @ConditionalonMissingBean - only create auto-configured bean if no user-specified bean is available
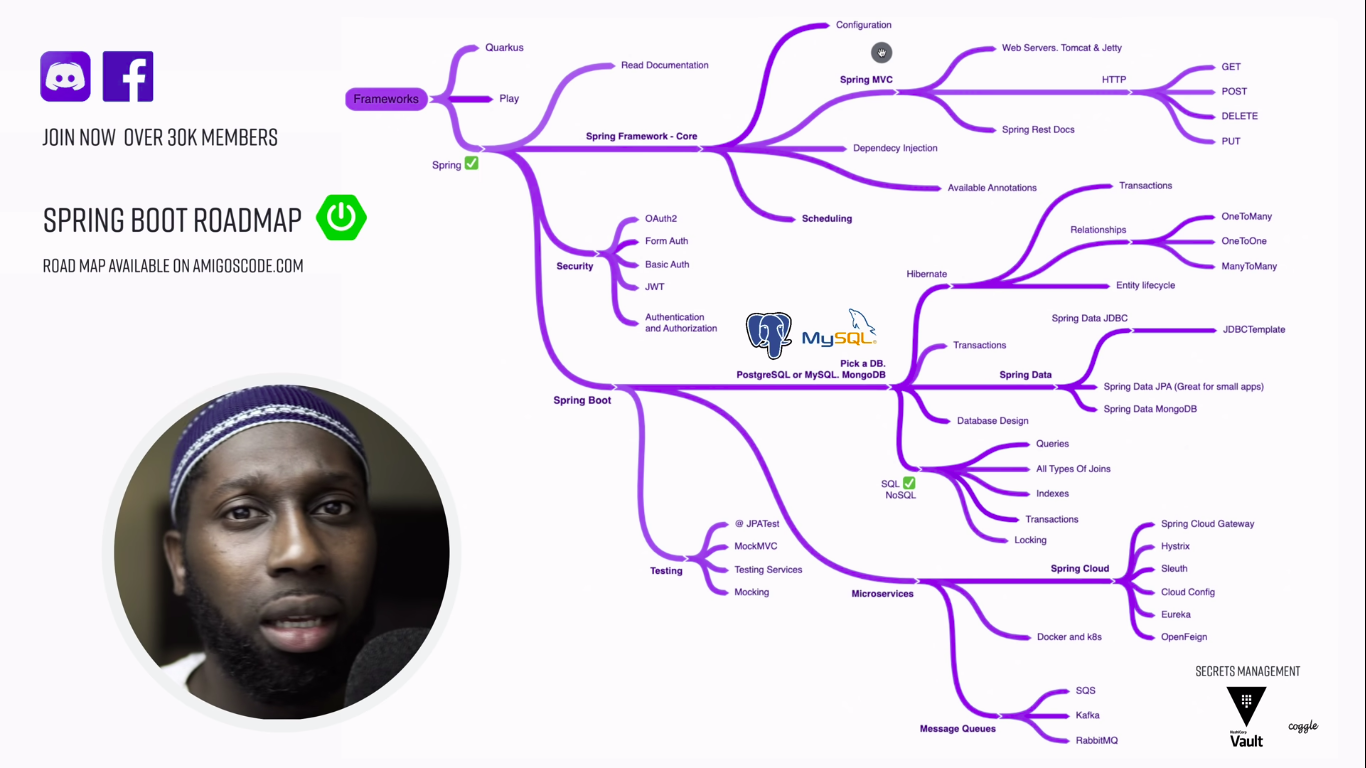
Spring Boot Microservices
*
Maven
- Article :
- POM - Project object Model
- war file - web archive files
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/maven-v4_0_0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<groupId>in.harshityadav</groupId>
<artifactId>mavenlearner</artifactId>
<packaging>war</packaging>
<version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version>
<name>mavenlearner Maven Webapp</name>
<url>http://maven.apache.org</url>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>junit</groupId>
<artifactId>junit</artifactId>
<version>3.8.1</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<build>
<finalName>mavenlearner</finalName>
</build>
</project>
Questions
What is Spring Beans?
Objects whose lifecycle is entirely managed by Spring
Which techniques using Spring will achieve inversion of control?
- Dependency Injection
- Factory Pattern
- Server Locator patter
What is Aspect-oriented programming?
- Adding functionality to existing code without changing the code itself
Which dependency management systems can be used with Spring?
- Gradle
- Maven
- Ivy
Model - Responsible for holding and updating application state
View - Responsible for presenting application state to the user
Controller - Holds the business logic of the application
What is the front controller in Spring MVC called?
- Dispatcher Servlet
Exercise to Self Learn and Practise :
- Create a Simple Spring Application using STS
- Create a Controller using Spring
- Create a REST Controller with getting Method
- Create a REST Controller with POST Method
- Use REST Template to access the endpoint
Questions
What annotation must be specified for the public class of your application to include Spring Boot? - @SpringBootApplication
- Dev Tools
- Cache Disabling
- Live Reload
Q. What is group id and Artifact ID?
Ans : groupId specifies the id of the project group while the artifactId specifies the id of the project.
Q. What is aspect orinted programming ?
Ans : In a typical enterprise application there are 3 layers
- UI Layer
- Business Layer
- Data Access Layer.
Across these threee layers there are some cross cutting functionalitty that are required in all the three layers like
- logging
- Profiling
- security
- transaction management
In “ Object oriented programaing “ there is a class and an object is the key unit that represents that class ,
in “ Aspect oriented programming “ there is aspect (key unit) or a specialised unit that address the cross cutting concern like onf of the 4 listed cross cutting functionlaity listed
- Through AOP we can address the concerning cross cutting functionality
- Reuse : Once we develope Aspect we can use it across enterprise application ,
- Quick Development : focus more on business logic and can add these functionality any point in time
- Focus on Aspect : one dev can focus and build on one aspect while the other dev can work on another
- Enabled / Disabled : Enabling and disabling aspects at runtime of the project during the configuration
Libraries that use AOP : Spring AspectJ
Q. What is dependency Injection ?
Ans : Dependency is basic things that a code depends upon to run. ( a computer needs a cpu and ram as dependency to run ) , one way to implement this in code is using dependency constructor ,
- With dependency injection , we inject the dependency into the class instead of preparing in the class which needs it
- No need to use “new” operator inside the class , or object of fancy container
- Pushing the dependency in the class model and accesing using the constructor parameter or via setter
Source : https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=IKD2-MAkXyQ&ab_channel=AnthonyFerrara
Q. What is Dependency Inversion Principle ?
Ans : Code shouldnt depend on depenendcy rather then its abstraction (Interface)
- By depending on Abstraction we we are decoupling on Implementation
Q. What is Dependency Injection Container ?
Ans. : It is a map of dependency that a class needs
- with the logic to create those dependency if they haven’t been created yet
So every time we ask for dependency while creating bean
The map will figure out which dependency to use
Containe will see if it has one of those dependency already , if yes it will use that one
If No , create dependency , store it
Q. What is Inversion of Control ?
Ans : Commonly we write and start our code , and move control to the library logic wherever needed and once that is needed the code execution flow is back in our code , in Ioc the framework starts and has the control flow and call our code whenver is needed and when our code use is over the flow goes back to the framework
Source : https://youtu.be/oLxsTnH_peI
in Spring. : dependency is with the interface
Q. Configuration,
- This annotation is the main artifact used by the Java-based Spring configuration; it is itself meta-annotated with @Component, which makes
- the annotated classes standard beans and as such, also candidates for component-scanning.
- The main purpose of @Configuration classes is to be sources of bean definitions for the Spring IoC Containe
Q. Autowiring
By declaring all the bean dependencies in a Spring configuration file, Spring container can autowire relationships between collaborating beans. This is called Spring bean autowiring.
After enabling annotation injection, we can use autowiring on properties, setters, and constructors.
Q. Application Context
Spring IoC container is responsible for instantiating, wiring, configuring, and managing the entire life cycle of objects.
BeanFactory and ApplicationContext represent the Spring IoC Containers.
ApplicationContext is the sub-interface of BeanFactory.
BeanFactory provides basic functionalities and is recommended to use for lightweight applications like mobile and applets.
ApplicationContext provides basic features in addition to enterprise-specific functionalities which are as follows:
- Publishing events to registered listeners by resolving property files.
- Methods for accessing application components.
- Supports Internationalization.
- Loading File resources in a generic fashion.